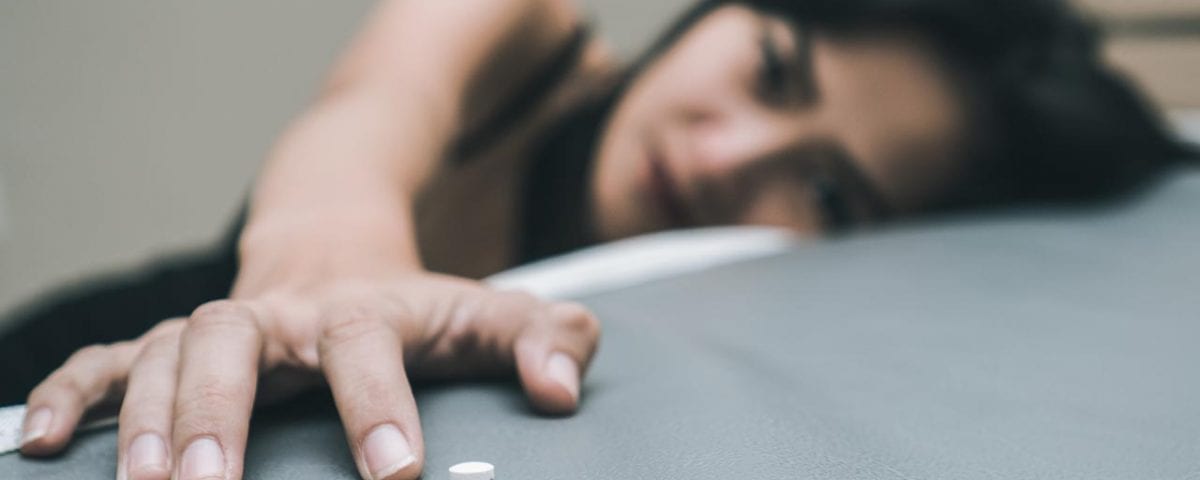
Ambien, also known as Zolpidem Tartrate, is a widely prescribed sedative-hypnotic medication for treating insomnia and other sleep-related disorders. Though effective in promoting sleep, Ambien has been associated with a range of unusual and sometimes dangerous behaviors, drawing significant media attention due to celebrity incidents and reports of bizarre actions carried out under the influence of the drug.
In this blog, we explore how Ambien works, the side effects, its potential for addiction, and how prescription pill addiction is treated.
How Does Ambien Work?
Ambien works by affecting the brain’s neurotransmitters, primarily gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). It binds to GABA receptors, producing a calming effect that slows brain activity, helping individuals fall asleep faster. While it functions similarly to benzodiazepines like Xanax, Ambien specifically targets sleep-inducing pathways, making it a sedative-hypnotic rather than an anti-anxiety medication. This makes it particularly effective for short-term treatment of insomnia by depressing the central nervous system and promoting restful sleep.
However, its impact on brain chemistry also carries certain risks, especially when misused or combined with other substances.
What Are the Side Effects of Ambien?
While Ambien is generally well-tolerated when used as prescribed, side effects can occur. The most common include:
- Dizziness
- Upset Stomach
- Daytime Drowsiness
- Lightheadedness
- Headaches
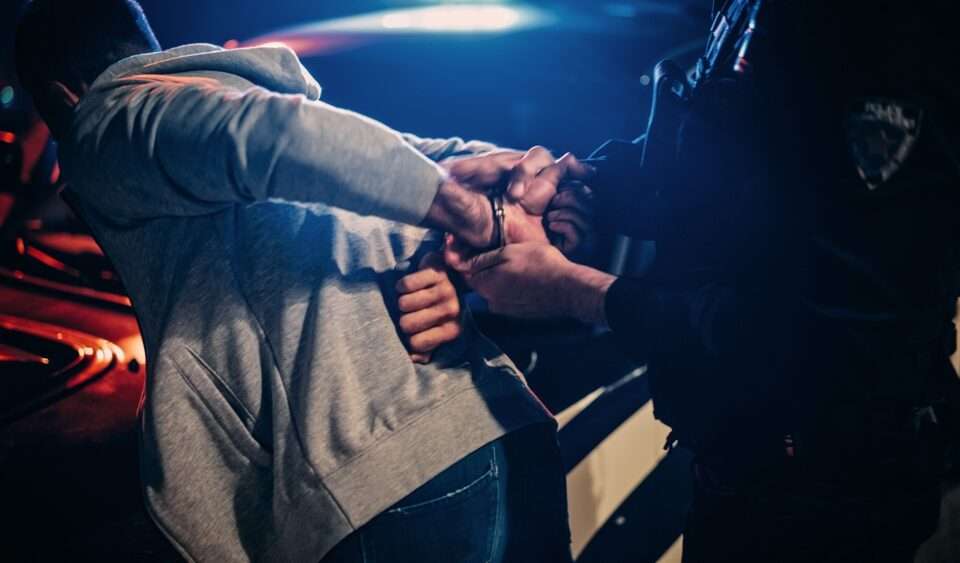
More concerning, however, are the rare but alarming side effects reported by some users. These can include engaging in complex behaviors—such as driving, preparing meals, or sleepwalking—without any recollection of the events afterward. This phenomenon is often referred to as "Ambien blackout," and in extreme cases, it has led to dangerous or even criminal behavior.
Additional severe side effects include:
- Behavioral Changes: Sudden mood swings, irritability, or increased aggression.
- Memory Impairment: Difficulty recalling events or confusion after waking.
- Ambien Hallucinations: Vivid, sometimes terrifying visions, visual hallucinations or auditory hallucinations.
While it is effective in promoting sleep and aiding sleep disorders, recent studies have highlighted novel clinical patterns associated with its use. These patterns include a range of side effects that may not be immediately apparent to both patients and healthcare providers.
One of the most intriguing patterns is the emergence of zolpidem induced hallucinations. Patients have reported experiencing vivid visual and auditory hallucinations, often described as dream-like or surreal.
Another clinical pattern involves behavioral changes, including sudden mood swings, irritability, and increased aggression. More alarmingly, some individuals engage in complex activities like preparing meals or driving without any memory of the events—a phenomenon known as zolpidem induced somnambulism. Such behaviors can have severe consequences, particularly when combined with other sedatives or alcohol.
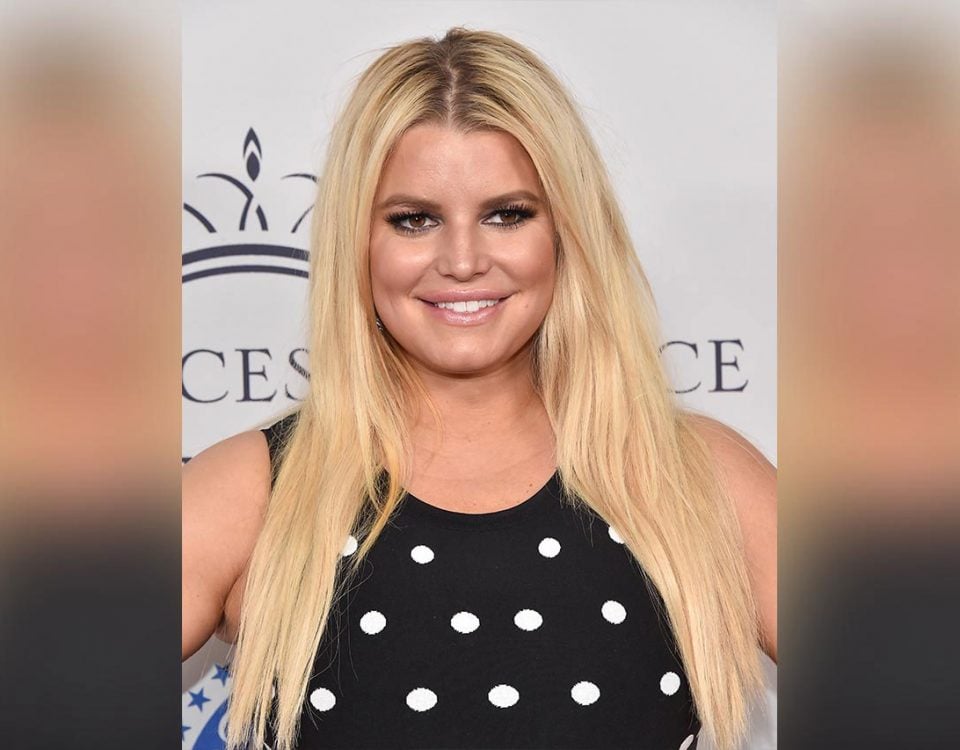
A highly publicized example of this was the case of actress Roseanne Barr, who in 2018 attributed a series of controversial tweets to Ambien intoxication, stating she was “Ambien tweeting.” While the pharmaceutical company responded that "racism is not a known side effect of Ambien," this incident brought to light how the drug could lead to unusual behavior.
Memory impairment and amnesia are other side effects that has gained attention. Patients may experience difficulty recalling events or confusion after waking, which can be distressing and impact daily functioning. These symptoms are often linked to the drug's impact on neurotransmitters and its potential interaction with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or other medications.
Questions about our Facilities or Programs?
Our admissions coordinators are available 24/7 to answer any questions you may have as you consider whether treatment at Banyan is right for you or your loved one.
Is Ambien Addictive?
Ambien is often marketed as a safer alternative to benzodiazepines, but it still carries significant risks when used long-term or improperly. Although it is less physically addictive than traditional benzodiazepines, dependence on Ambien can develop, especially when misused or taken in higher-than-prescribed doses.
Psychological dependence can also occur, with users believing they cannot sleep without the medication. Over time, tolerance builds, leading to increased dosages and higher risks of side effects, withdrawal symptoms, or addiction.
Some signs of Ambien dependence or misuse include:
- Increased Dosage: Regularly taking higher doses than prescribed or using the medication more frequently than directed. This may indicate a growing tolerance to the drug.
- Cravings and Preoccupation: Persistent cravings for Ambien or preoccupation with obtaining the medication. Individuals may spend excessive time thinking about or planning to acquire more Ambien.
- Behavioral Changes: Noticeable shifts in behavior, such as mood swings, irritability, or aggression. This can be particularly evident if these changes occur after taking Ambien.
- Difficulty Functioning Without the Drug: Struggling to fall asleep or maintain normal sleep patterns without Ambien. This includes experiencing severe insomnia or anxiety when not using the medication.
- Neglecting Responsibilities: Failing to fulfill work, academic, or personal responsibilities due to the effects of Ambien. This might include missing appointments, neglecting duties, or experiencing frequent absences.
- Using Ambien Illicitly: Engaging in activities like doctor shopping to obtain prescriptions from multiple doctors, or acquiring Ambien through illegal means.
- Physical Symptoms: Experiencing withdrawal symptoms when not using Ambien, such as anxiety, tremors, or rebound insomnia. These symptoms can signal physical dependence on the drug.
- Memory Problems and Bizarre Behavior: Engaging in unusual or dangerous activities, like sleepwalking or driving, without memory of these actions. This behavior is often linked to Ambien’s effects on the brain and can be a sign of misuse or addiction.
- Secretive Behavior: Hiding the use of Ambien or lying about how much or how often it is used. This may include concealing medications or avoiding conversations about drug use.
- Continued Use Despite Negative Consequences: Persisting in using Ambien despite experiencing adverse effects, such as relationship problems, legal issues, or health concerns.
Treatment for Ambien Addiction
Like other prescription pill addictions, Ambien misuse should be treated under professional care, particularly through a medically supervised detox. Abruptly stopping Ambien can lead to withdrawal symptoms, including severe insomnia, anxiety, or even seizures. A structured detox process is crucial to manage these symptoms and prevent relapse.
At Banyan Treatment Centers, we provide comprehensive programs designed to support individuals in overcoming prescription medication dependence. Our detox and rehabilitation services are customized to meet each patient’s unique needs, ensuring a safe and supportive environment for achieving long-term sobriety. We combine evidence-based therapeutic practices with holistic treatments tailored to each person’s requirements. If you or a loved one is struggling with addiction to sedative-hypnotics like Ambien, our professional treatment programs are here to guide you on the path to recovery.
Getting into treatment is easy with our free insurance verification
"*" indicates required fields
Contact Us Today
If you are concerned about your use of Ambien or any other sedative-hypnotics, don't hesitate to seek help. Call Banyan Treatment Centers at 888-280-4763 to learn more about our addiction treatment services and take the first step toward lasting recovery.
Sources:
- Huffington Post – The Disturbing Site Effect of Ambien
- ABC News – What is Ambien and what are its known side effects?
- Women’s Health – 10 Side Effects of Ambien that are Actually Pretty Terrifying
- Fox News – Roseanne Barr not first celeb to claim Ambien led to bizarre behavior: What is the insomnia drug?