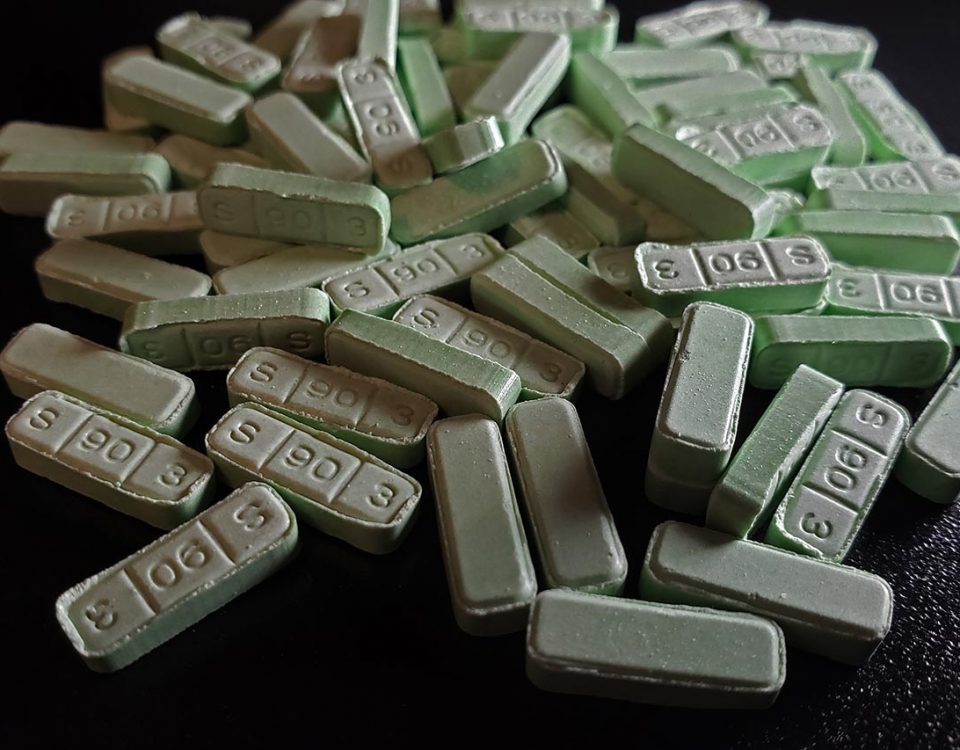
Methamphetamine is a highly addictive and dangerous central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that’s illegally made and sold in drug markets.
Meth is usually made in illicit meth labs and is produced by distilling a combination of harsh chemicals and medications like codeine and fentanyl. But what do they cut meth with aside from other drugs? Since little is known of meth’s production process, crystal meth ingredients are often rearranged to intensify the drug’s side effects and allow dealers to sell less of the actual drug for more money. As a drug rehab in Boston, we know that what meth is cut with plays a huge role in its potential for abuse and overdose. We’re sharing an overview of common ingredients in meth as well as its cutting agents.
Purpose of Meth Cutting Agents
Methamphetamine sold on the streets isn’t just dangerous alone, but its cutting agents or additives can make the drug even more threatening to the body. Cutting agents are additional chemicals or drugs used in the production process to cheapen and shorten production while allowing dealers to make more profit with less product. Most cutting agents are chosen for their similar appearance to methamphetamines, such as white powders like talc and milk powders. Addicting cutting agents to meth also makes the product weigh more. If a dealer buys one kilogram of methamphetamine and sells 1.5 kilograms of contaminated meth at the going price, they’ll make more money. Some drug suppliers will also add additional substances to enhance the side effects of meth. Additionally, meth usually passes through many hands, starting from the actual manufacturer and through several dealers, increasing the likelihood of containing additives.
Regardless of the reason behind cutting agents in meth, these agents are often indistinguishable from the pure product without a formal lab test. These additives also have the potential to produce a negative reaction or toxicity that’s even deadlier. Without meth addiction treatment, users are less likely to quit and recover from the side effects of this drug.
What Do They Cut Meth With?
So, what do people cut meth with? Meth can be cut with different substances. Methamphetamine can be diluted with powders and even household chemicals to increase its weight. Other drugs or medications like codeine and fentanyl are also often used as meth cutting agents to add to the drug’s potency and side effects. Metal impurities also often make their way into the product during production.
Powdery Substances
Commonly used meth cutting agents include powdery substances like baby powder, baking soda, or powdered milk. Although these additives are harmless compared to metals or drugs, these products can clog arteries and contribute to cardiovascular disease and other health complications. However, because most of these substances are similar in color to meth, they blend in easily with the drug when sold in white powder or tablet form. Smoking is the most common way to use meth, and these additives can irritate the lungs and increase the likelihood of respiratory infection and other related diseases. These additives can also add solid particles to the bloodstream, putting users at risk of stroke and heart attack.
Other Drugs
Meth is made with pseudoephedrine and ephedrine products, so other similar ingredients often end up as cutting agents in meth. These medicines can range from cough and cold medicines to pain relievers to dietary supplements. Many of these products also have a potential for abuse and produce side effects. Some common drugs used in meth include:
- Codeine
- Fentanyl
- Acetaminophen
- Caffeine
- Phenacetin
- Ambroxol
- Chlorpheniramine
- Desloratadine
- Barbital
- Ketamine
- Procaine
- Dimethyl Sulfone
Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM)
MSM is a supplement that’s most commonly used to strengthen cartilage in the body. It’s usually sold in the form of a white powder that looks similar to meth when processed, which is why it’s the most common cutting agent in meth. Like other additives, the MSM cutting agent in meth adds weight to the product, convincing users that they’ve purchased more product than they actually have.
Isopropylbenzylamine
Isopropylbenzylamine is a chemical that’s often used as an intermediate product in the synthesis of pharmaceutical drugs. However, because it’s often used to dilute meth, this chemical is currently under the consideration of the DEA.
Metals
Metals like palladium, lithium, and nickel are often used in the meth production process. Even though these metals aren’t detectable in final products, they’re simply used to add weight. Like other additives, metals in meth can cause neurological problems and kidney damage.
Other common meth cutting agents include lithium metal, hydrochloric acid, iodine, sulfuric acid, and red phosphorus. What meth is cut with increases its dangers, such as addiction, mental illness, cardiovascular disease, stroke, heart attack, overdose, and death. Meth’s effects on the brain and neurotransmitters like dopamine encourage users to continue their drug habits, despite the obvious dangers. Methamphetamine’s mechanism of action makes it highly addictive, and users who do not receive PHP treatment are less likely to recover.
The rise of meth use and other forms of substance abuse is a growing concern in the United States. If you or someone you know has a drug problem, Banyan Massachusetts can help. We have years of experience treating individuals with various kinds of addictions to physically and mentally recover from drugs and alcohol. Call us now at 888-280-4763 for more information about our addiction treatment in Massachusetts.